What is the Goal Gradient Effect?
Coined by behaviorist Clark Hull in 1932, the Goal Gradient Effect states that as people get closer to a reward, they speed up their behavior to get to their goal faster. In other words, people are motivated by how much is left to reach their target, not how far they’ve come.
As Hull put it in his original research:
“Rats in a maze run faster as they near the food box than at the beginning of the path.”
4 Examples of the Goal Gradient Effect in Action
The closer customers get to their goal, the more encouraged they become to finish. But they can’t get motivated if they don’t know where the finish is.
For this reason, you’ll often see the Goal Gradient Effect at work in gamification elements like progress bars, badges, and profile completion percentages. It can be applied anywhere users are encouraged to complete a big task by achieving smaller objectives.
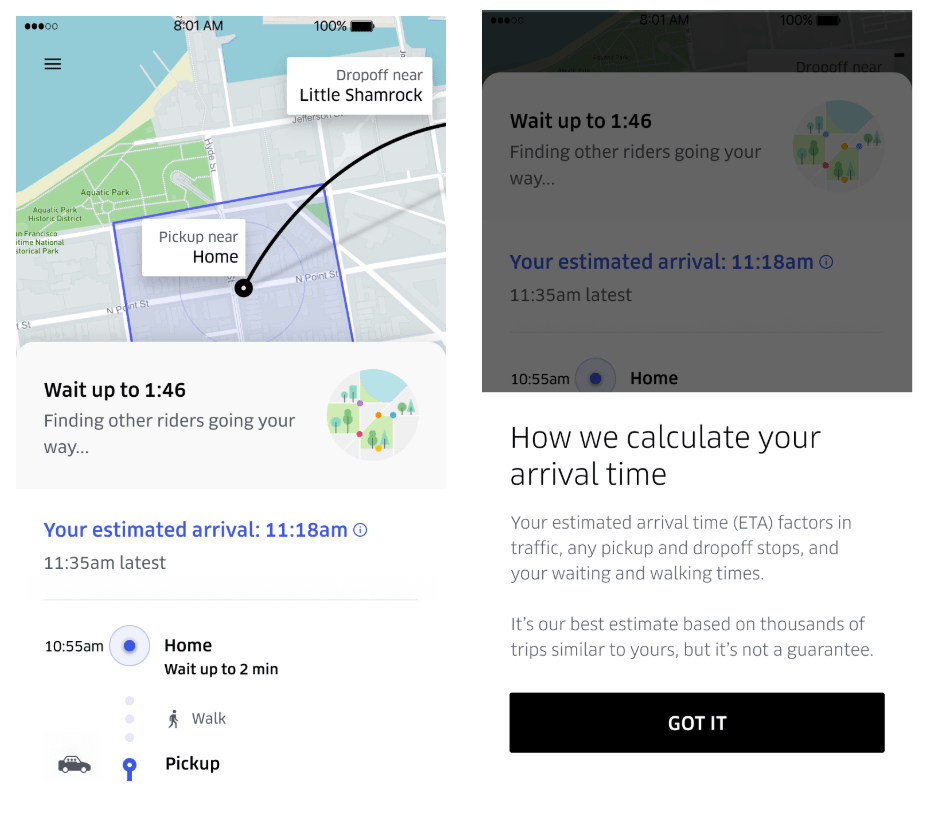
1. Uber: Using gamification to make progress clear
The biggest pain point for Uber customers is waiting for their ride. To make the time pass more quickly, Uber uses a car animation on a map to indicate progress.
This application of the Goal Gradient Effect is interesting because it isn’t driving customers to complete a checkout process or finish filling out their dating profile. Instead, this use of the Goal Gradient can change customer perceptions of time by providing a transparent waiting process. The closer your Uber gets to you, the faster the time seems to pass.
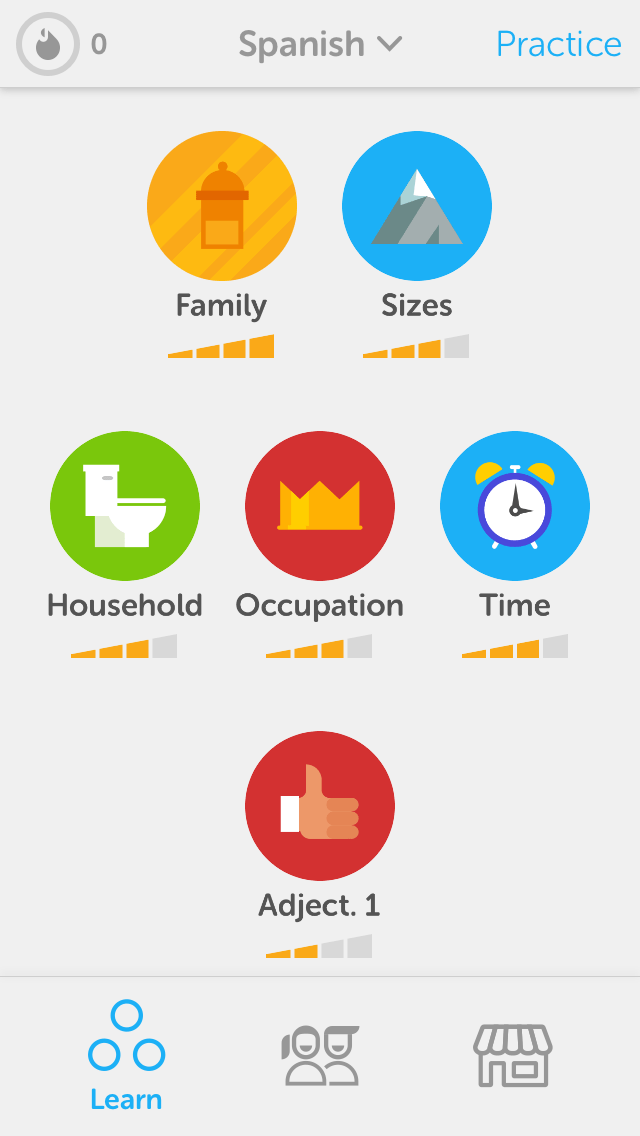
2. Duolingo: Using “chunked” progress bars to drive engagement
Duolingo is a master of using the Goal Gradient Effect to keep people engaged. Each section of the material is broken down into smaller subsections, each with its own mini progress bar.
Duolingo combines the Goal Gradient Effect with chunking, a psychological learning technique. Chunking is a process by which big groups of information (the Spanish language, for example) are broken down into smaller parts. Then these parts are grouped by common elements. In the case of Duolingo, they chunk subjects into smaller topics like “Family,” “Time,” and “Sizes.”
By combining the Goal Gradient Effect and chunking, Duolingo creates an experience that makes it easy for users to stick to learning a language.
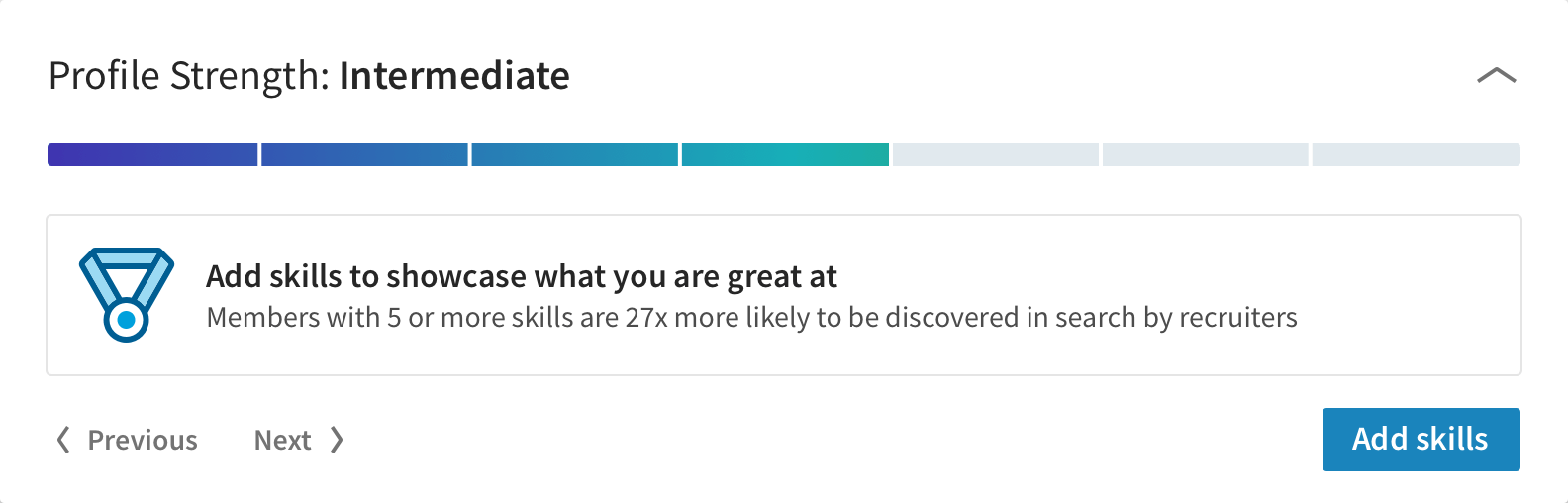
3. LinkedIn: Using Progress bars to drive profile completion
One of the most common applications for the Goal Gradient Effect is in UX elements that show progress, such as the “Profile Strength” element on LinkedIn. By tying a progress bar to a measure of completeness, “Intermediate,” for instance, LinkedIn has made customers more likely to complete their profile.
For added measure, they’ve combined the Goal Gradient Effect with data to persuade users that their work will help them be “discovered in search by recruiters.” By tying users’ profile completeness to the end goal of a new job, LinkedIn makes it clear that their goal is closer than they think.
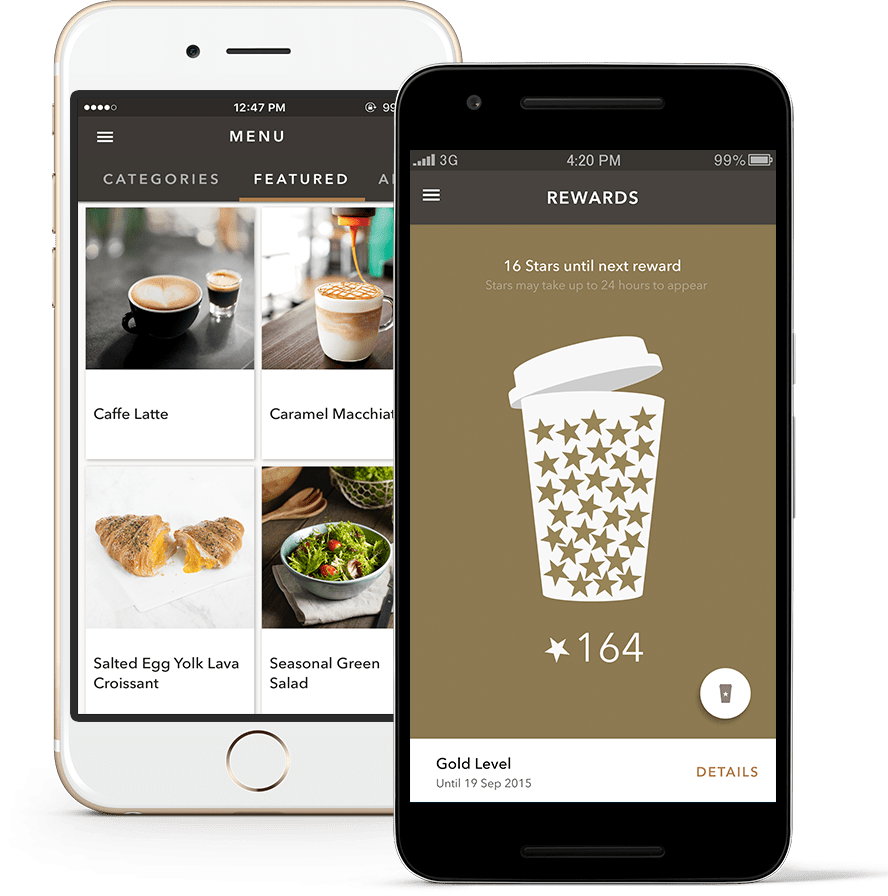
4. Starbucks: Using using loyalty cards to drive purchase
The application of the Goal Gradient Effect in loyalty programs has been well researched. Here, Starbucks has combined a compelling visual experience in their app with the power of behavioral science.
The Starbucks app drives customers to buy more coffee with Goal Gradient language such as “16 stars until next reward”. Everything in the experience pushes customers to keep buying until they achieve their goal.
How to Get Started Applying the Goal Gradient Effect
The Goal Gradient Effect is a useful tool to drive customer engagement in both physical and digital touchpoints. If you’re looking for places to apply Goal Gradient, think about where customers tend to drop off in your experience and might need a little extra motivation.
To apply the Goal Gradient Effect, start by asking yourself:
- Do we have a visual representation of a customers' progress in our experience? These could include badges, progress bars, or achievements.
- When we remind a customer that they've left something in their cart, does our language reflect how close they are to reaching their goal?
- If we have a loyalty program, what would be the effect of seeding in credit for the first few purchases (randomly giving two stamps for one coffee, for example)?
Want to learn more about how your buyers tick (using marketing psychology, behavioral science, and predictive AI)?
👉 When you’re ready, Choice Hacking can help:
- Coaching: Looking for clarity, focus, and confidence in your marketing and/or career? Behavioral Science-powered 1-on-1 Coaching could be a good match for you.
- Courses & Skill Sessions: Improve your customer experience, customer journey maps, presentations, landing page conversion rate, and more with the power of applied behavioral science in a self-directed course.
- Training: We can help your team level up their work with psychology, behavioral science, and AI training.
- Consulting: Get professional insight to grow your business with projects like:
